Pathology Of Parkinson's Disease
Pathology of parkinson's disease. In Parkinsons disease PD in addition to degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway a variety of neuronal systems are involved causing multiple neuromediator dysfunctions that account for the complex patterns of functional deficits. Parkinsons disease PD or simply Parkinsons is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. Parkinsons disease PD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease characterized typically by motor features of tremor rigidity and bradykinesia due to depletion of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons.
PARKINSONS DISEASE DIFFUSE LEWY BODY DISEASE. Pathology anatomy and behavior Neuropsychiatric and Cognitive Changes in Parkinsons Disease and Related Movement Disorders Diagnosis and Management. PD is associated with motor symptoms including tremors and stiffness that affect balance and coordination.
The disease was first described in 1817 by British physician James. In 1997 a mutation was identified in the alpha-synuclein gene. However hallucinations delu-sions irritability apathy and anxiety also have been re-ported1Herewewillcommentonthemostprevalent ofthesesymptoms.
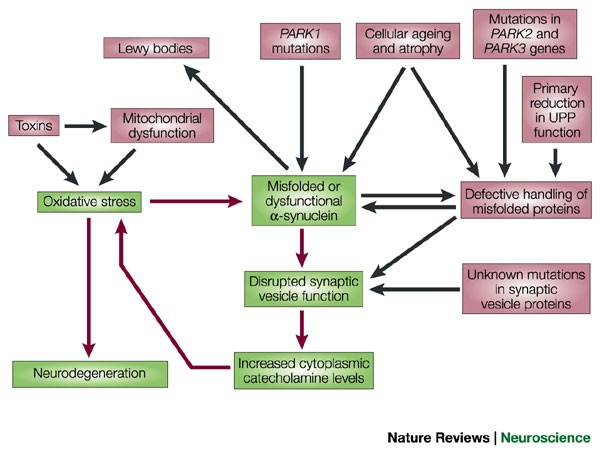
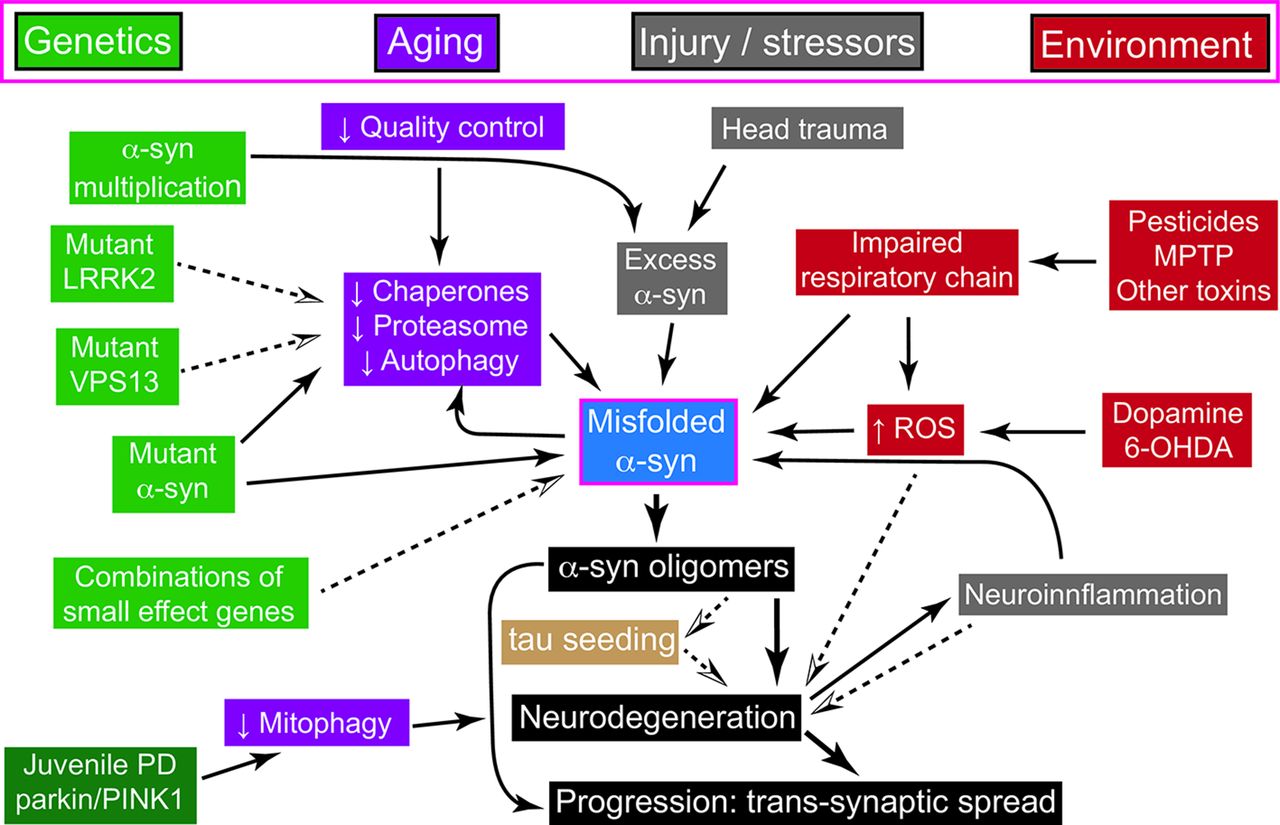
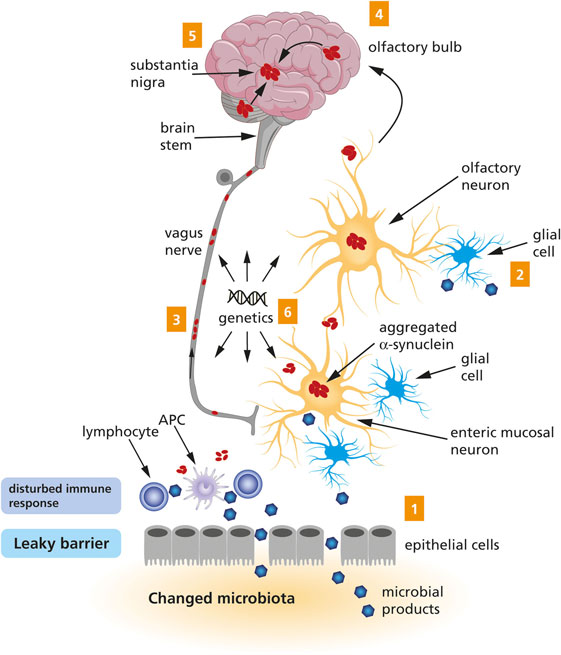
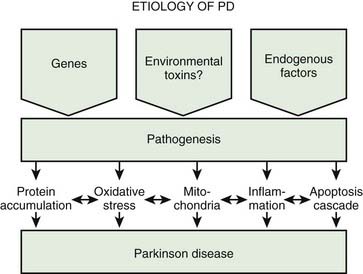
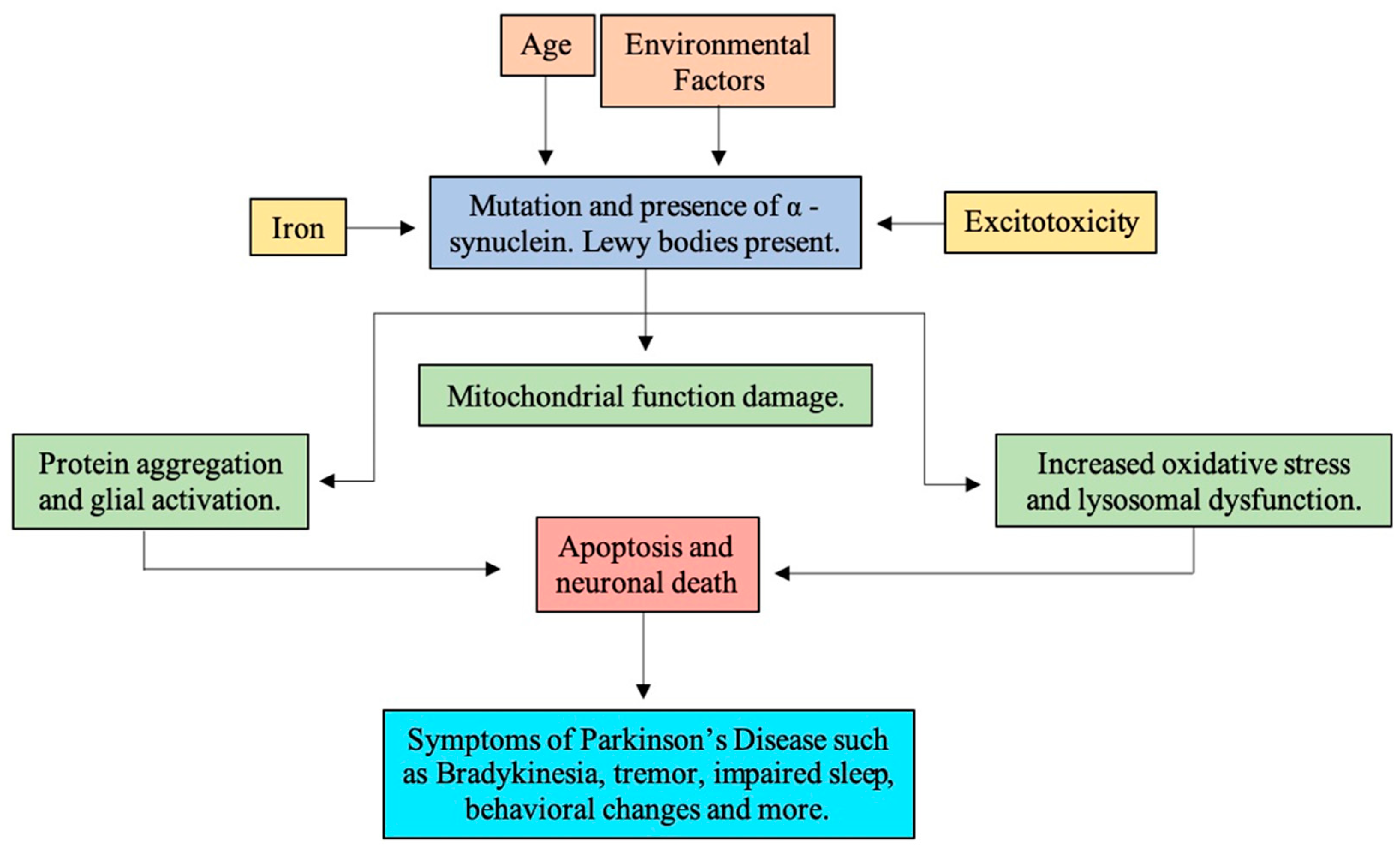
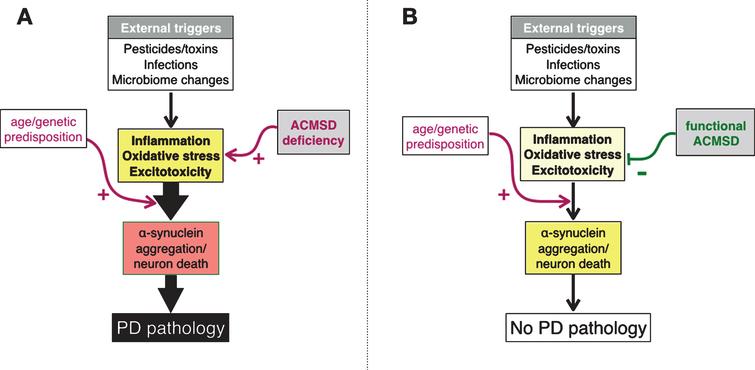
Many environmental and genetic factors influence Parkinson disease risk with different factors predominating in different patients. Symptoms appear as dopaminergic neurons are lost from the midbrain. In idiopathic Parkinsons disease PD α-synuclein accumulates in neuronal perikarya Lewy bodies and neuronal processes Lewy neurites.
PD is a progressive disorder with a mean onset age of 55 years. Parkinsons disease PD is a common neurodegenerative disorder of unknown cause that occurs in adults. The primary pathology of PD is the.
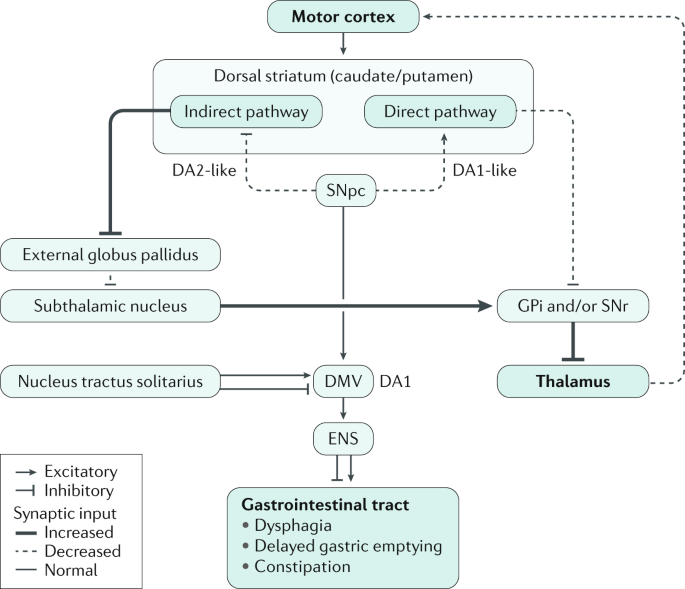
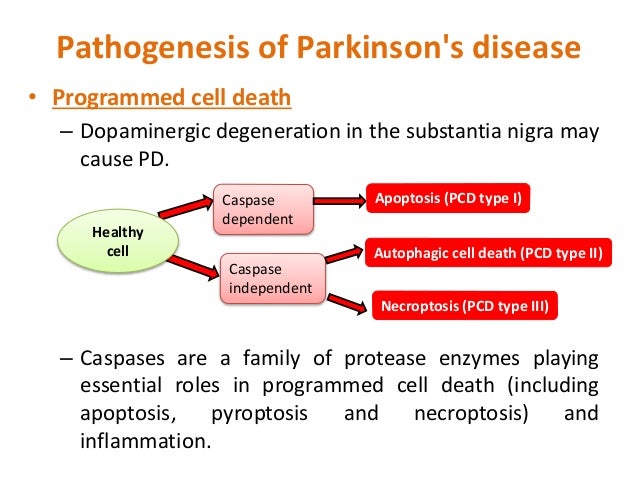
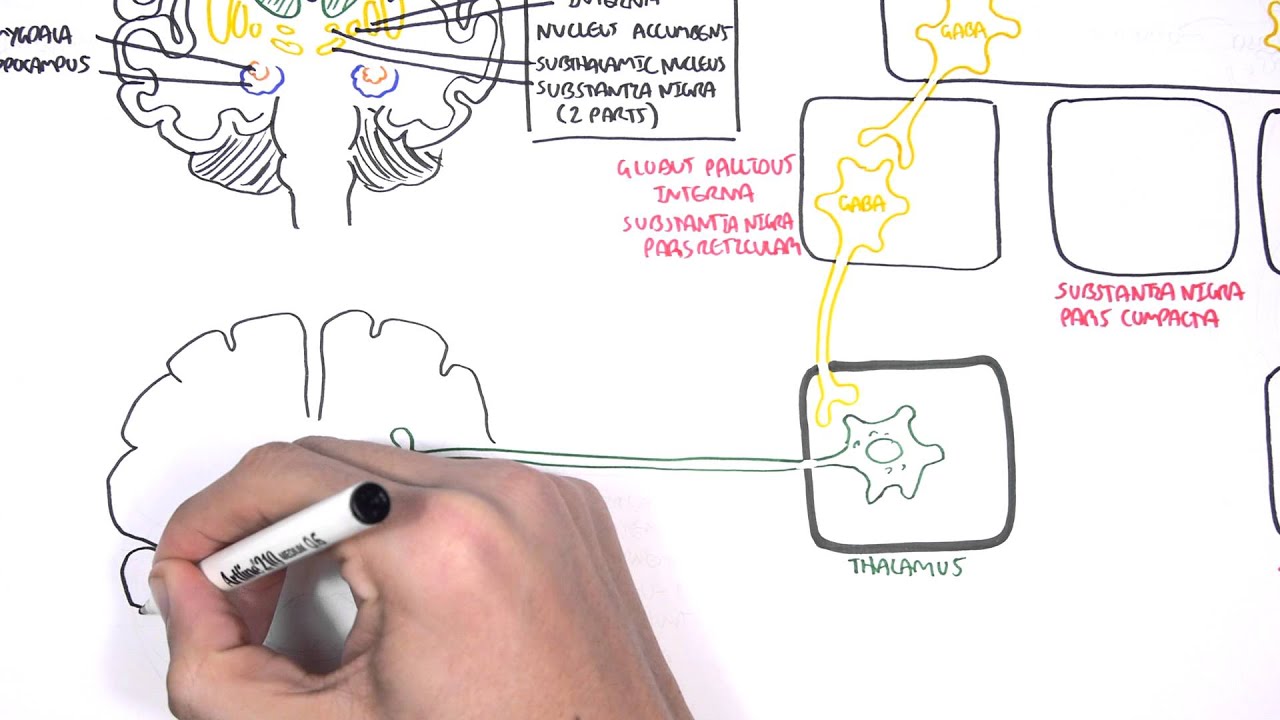
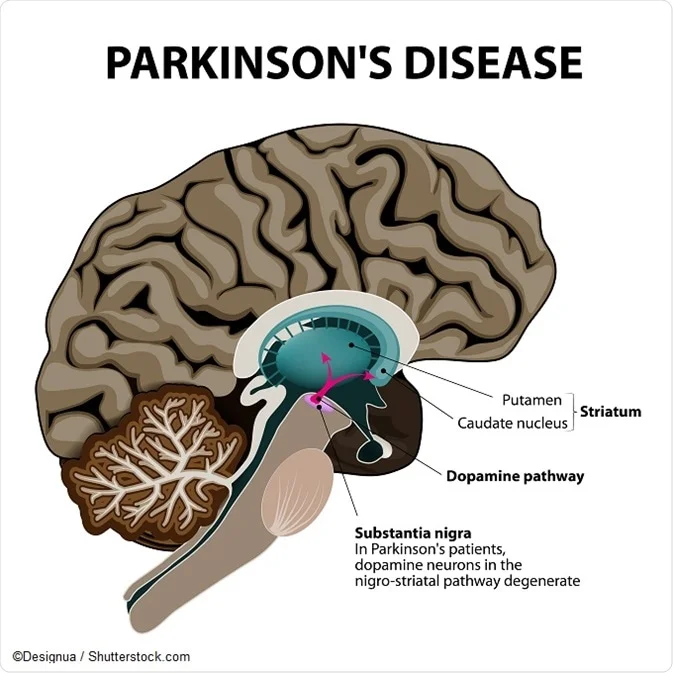
Traditionally PD has been viewed as a specific entity in which clinical parkinsonism rigidity bradykinesia and tremor is associated with the pathological findings of neuronal loss and Lewy bodies in the substantia nigra. This results in overall decreased motor cortical stimulation due 1 lack of direct pathway stimulation leading to decreased movement and 2 lack of inhibition of the indirect pathway leading to increased inhibition of movement. In Parkinsons Disease loss of dopaminergic neurons occurs in the nigro-striatal pathway.
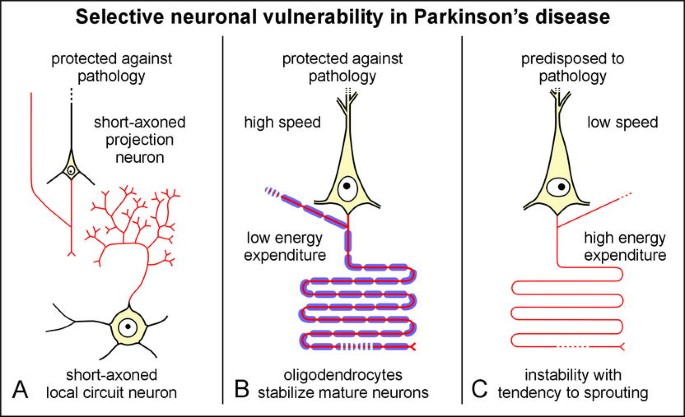
The symptoms usually emerge slowly and as the disease worsens non-motor symptoms become more common. PD is pathologically characterized by the loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic innervation although neurodegeneration is not limited to only the nigral dopaminergic neurons but also involves cells located in other regions of the neural network.
The primary pathology of PD is the.
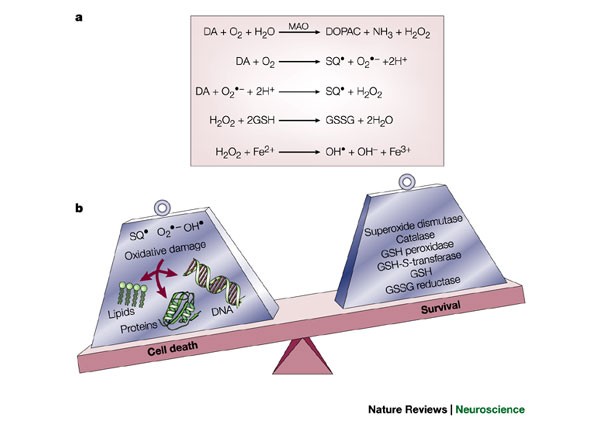
The symptoms usually emerge slowly and as the disease worsens non-motor symptoms become more common. PARKINSONS DISEASE DIFFUSE LEWY BODY DISEASE. These factors converge on specific pathways including mitochondrial dysfunction oxidative stress protein aggregation impaired autophagy and neuroinflammation. PD is pathologically characterized by the loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic innervation although neurodegeneration is not limited to only the nigral dopaminergic neurons but also involves cells located in other regions of the neural network. PD is a progressive disorder with a mean onset age of 55 years. This results in overall decreased motor cortical stimulation due 1 lack of direct pathway stimulation leading to decreased movement and 2 lack of inhibition of the indirect pathway leading to increased inhibition of movement. Parkinsons disease PD or simply Parkinsons is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. Parkinson disease also called primary parkinsonism paralysis agitans or idiopathic parkinsonism a degenerative neurological disorder that is characterized by the onset of tremor muscle rigidity slowness in movement bradykinesia and stooped posture postural instability. Complex I Inhibition.
In Parkinsons disease PD in addition to degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway a variety of neuronal systems are involved causing multiple neuromediator dysfunctions that account for the complex patterns of functional deficits. The symptoms usually emerge slowly and as the disease worsens non-motor symptoms become more common. Diffuse Lewy body disease DLBD Lewy body dementiais a sporadic neurodegenerative disease. PARKINSONS DISEASE DIFFUSE LEWY BODY DISEASE. PD is a progressive disorder with a mean onset age of 55 years. However hallucinations delu-sions irritability apathy and anxiety also have been re-ported1Herewewillcommentonthemostprevalent ofthesesymptoms. This results in overall decreased motor cortical stimulation due 1 lack of direct pathway stimulation leading to decreased movement and 2 lack of inhibition of the indirect pathway leading to increased inhibition of movement.































Post a Comment for "Pathology Of Parkinson's Disease"